This is the multi-page printable view of this section.
Click here to print.
Return to the regular view of this page.
Subclusters in MC
In Eon Mode databases, you can use subclusters (groups of nodes) to separate different workloads, to control how those workloads use resources, and to facilitate scaling your database up and down as workloads fluctuate.
In Eon Mode databases, you can use subclusters (groups of nodes) to separate different workloads, to control how those workloads use resources, and to facilitate scaling your database up and down as workloads fluctuate. This allows you to better manage your cloud resource expenses or data center resources. For an overview of subcluster concepts and how subclusters work, see Subclusters.
MC makes it easy to view and manage your subclusters. You can track how queries are performing and how well your subcluster resources are balanced. Using MC, you can use the information to adjust the number and size of your subclusters to improve your query throughput and system performance.
Visualizing your subclusters
The charts on the Database Overview page allow you to view and drill down into the resource usage of your database at any level. You can look at the resource usage of all nodes, or all subclusters, or individual subclusters. For details, see Charting subcluster resource usage in MC.
You can view statistics for the individual nodes in each subcluster in table format on the Database Manage page, in the Subclusters tab.
For a tour of the monitoring features of the Manage > Subclusters tab, see Viewing subcluster layout in MC.
Managing your subclusters
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
For Enterprise Mode databases, MC supports these actions:
Note
In the cloud on GCP, Enterprise Mode databases are not supported.
To view and manage your subclusters, select your database from the MC Home page or the Databases and Clusters page. MC displays your database's Overview page. Select Manage at the bottom of the Overview page.
To view the Subclusters page, click the Manage > Subclusters tab:
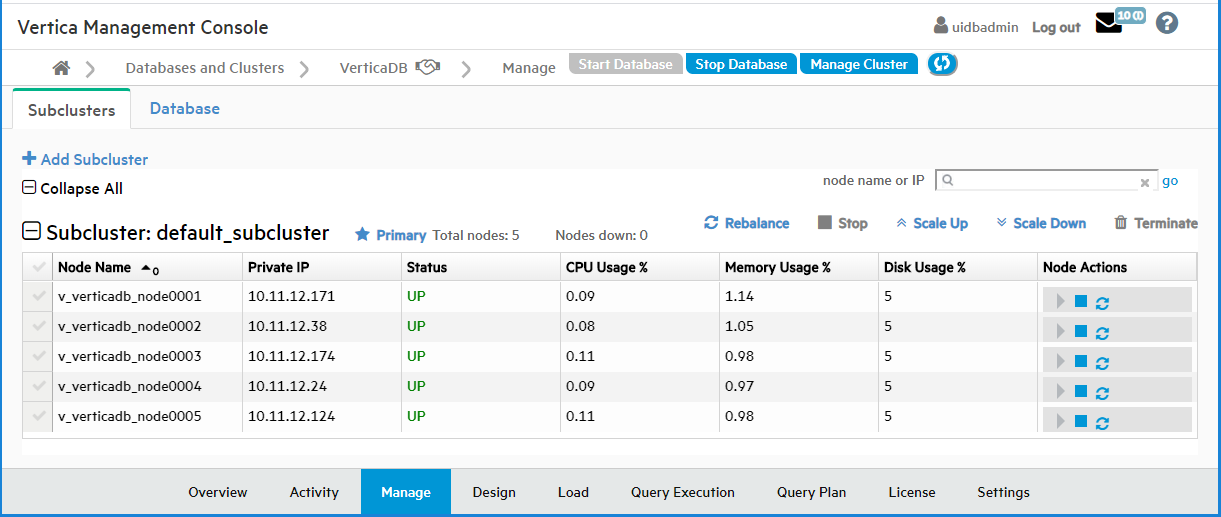
Eon Mode in the cloud
In Eon Mode on cloud platforms, you can use the Manage > Subclusters tab to add subclusters, rebalance your subclusters, stop and start subclusters, scale subclusters up or down, or terminate a subcluster. You can also stop or start a node, or restart a database node and its underlying instance.
Eon Mode on-premises
In Eon Mode on-premises, available subcluster and node actions behave a little differently than in the cloud, because your Vertica nodes reside on actual machines in your data center rather than on cloud instances.
Subcluster Actions in Eon Mode on Premises
-
In Eon Mode on-premises, you can use the Manage > Subclusters tab to add subclusters, rebalance your subclusters, or delete a subcluster.
-
You can add (create) a subcluster only if additional Vertica host machines are available.
-
When you delete a subcluster, MC deletes the subcluster from the database but does not delete the actual machines. MC stops the nodes in the subcluster, removes them from the subcluster, and deletes the subcluster. The Vertica host machines are then available to be added to other subclusters.
-
When you start or stop a subcluster in an Eon Mode database on-premises, MC starts or stops the subcluster nodes on the Vertica host machines, but not the machines themselves.
-
When you scale up a subcluster on-premises, the MC wizard displays a list of the available Vertica host machines that are not currently part of a database. You select the ones you want to add to the subcluster as nodes, then confirm that you want to scale up the subcluster.
When you scale down a subcluster on-premises, MC removes the nodes from the subcluster in the database, but does not terminate the Vertica host machines. The hosts are now available for scaling up other subclusters.
-
Scale Up displays the IP addresses of all available Vertica hosts that are not part of the database. The Scale Up button is grayed out if there are no Vertica hosts in the cluster that are not part of the database.
Node actions in Eon Mode on premises
When you start or stop a node on-premises, MC starts or stops the node in the database, but does not start or stop the Vertica host machine. The Restart Node action is not available for on-premises Eon Mode databases.
1 - Charting subcluster resource usage in MC
On the Database Overview page, in the CPU/Memory/Disk I/O chart and the Database General Pool Usage chart, you can use the dropdown in the title bar to focus the chart on:.
On the Database Overview page, in the CPU/Memory/Disk I/O chart and the Database General Pool Usage chart, you can use the dropdown in the title bar to focus the chart on:
-
All nodes in the database
-
All subclusters in the database
-
An individual subcluster, by name
For example, the CPU/Memory/Disk I/O chart dropdown allows you to choose the database nodes, one named subcluster, or all subclusters.
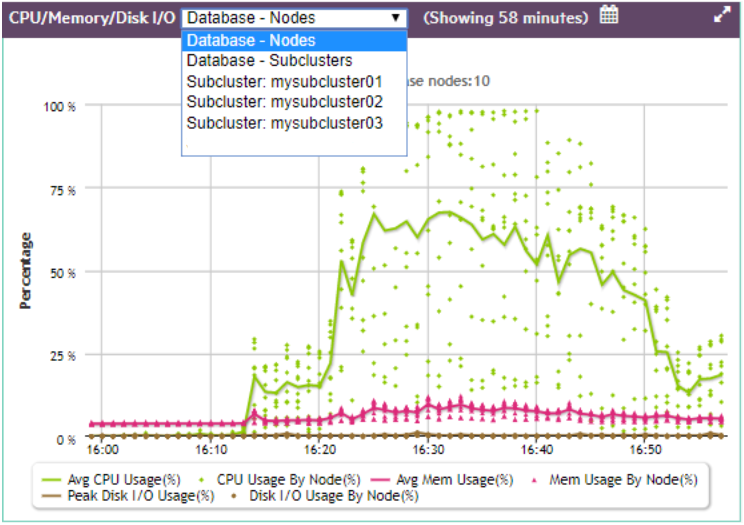
If you choose Database - Subclusters, the line in a given color represents the trend of all subclusters averaged together for that statistic, and each dot of the same color represents an individual subcluster at a certain time, for that same statistic.
For more in-depth information on how expand detail areas of charts and drill into the details, see Viewing the overview page.
2 - Viewing subcluster layout in MC
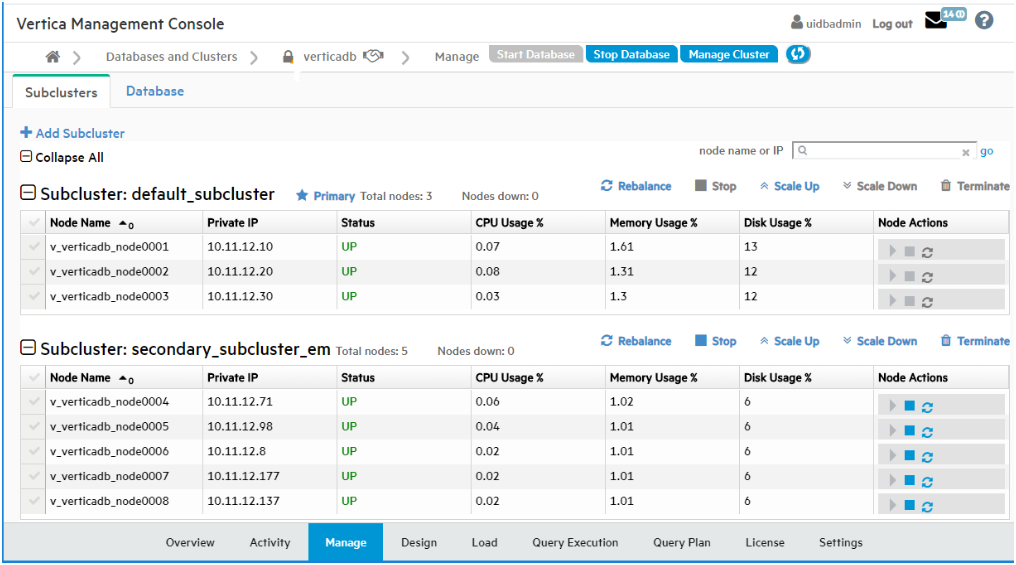
The MC Database Manage page displays two tabs, the Subclusters tab and the Database tab.
The MC Database Manage page displays two tabs, the Subclusters tab and the Database tab.
This topic describes the monitoring functions of the Subclusters tab. To monitor your subclusters, on the Subclusters tab you can view, sort, and search for subclusters and view their layout and statistics.
For information about using the Subclusters tab to make changes — adding, rebalancing, stopping and starting, scaling up or down, or terminating subclusters — see Subclusters in MC and its subtopics.
The Subclusters tab includes the following statistics in table form for the nodes in each subcluster:
-
Node name
-
Private IP address
-
Status (UP or DOWN)
-
CPU Usage %
-
Memory Usage %
-
Disk Usage %
Searching for nodes
To find a particular node, enter its node name or IP address in the "node name or IP" search field at the top right of the Subclusters tab. Searching for nodes is especially helpful if your cluster is very large. To find a specific node, enter its complete node name or IP address. You can enter a partial node name or IP address to find all nodes whose name or IP address contains that string. For example, if you enter "240" in the search field, MC would find both of the following nodes:
Note
Wildcard characters are not supported in the search field.
Starting, stopping, or removing nodes
The right column provides icons for executing node actions. You can start, stop, or remove a node in the subcluster. Removing a node also removes it from the database. Only the Start, Stop, and Remove actions are available on this page. For details, see Starting, stopping, and restarting nodes in MC
Note
If you change the layout of your subcluster, for example by removing nodes, you must rebalance shards. See
REBALANCE_SHARDS.
Sorting nodes within a subcluster
You can sort the nodes within each subcluster by the values in any column, by clicking on the column heading.
Collapsing or expanding a subcluster, or the entire table
To collapse a subcluster section to one summary row, click the minus icon or the subcluster heading. To collapse the entire table to summary rows, click the minus icon or "Collapse All".
To expand a collapsed subcluster section, click the plus icon or the subcluster heading. To expand the entire table, click the plus icon or Expand All.
3 - Adding subclusters in MC
You can add a subcluster to an Eon Mode database on-premises or in the cloud, to provide your database with more compute power, and to separate workloads.
You can add a subcluster to an Eon Mode database on-premises or in the cloud, to provide your database with more compute power, and to separate workloads.
For more information about the rules governing subclusters, see Subclusters.
When you use MC to add an Eon Mode subcluster on a cloud platform, MC provisions the requested instances, configures them as nodes in your database cluster, and forms those nodes into a new subcluster.
You can add a second primary subcluster in order to stop the original primary. Be sure to make the replacement primary subcluster at least one node larger than the original. (If you make them the same size, they both count equally toward the quorum, and stopping either would violate the quorum, so you cannot stop either one. For more information, see Data integrity and high availability in an Eon Mode database.)
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
The following steps add a subcluster on AWS:
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Add Subcluster to open the Add Subcluster window.
-
On Enter AWS Credentials and preferences, some values might populate based on your current configuration. Accept the defaults or enter the following values:
-
AWS Region: Enter the same region as your cluster.
-
AWS Subnet: The subnet for your cluster. By default, Vertica creates your cluster in the same subnet as your MC instance.
Important
Use security groups and network access control lists (ACLs) to secure your subnet. For details, see the
Amazon documentation.
-
AWS Key Pair: Your Amazon key pair for SSH access to EC2 instances.
-
Select Next. On the Specify Subcluster Information screen, supply the following information:
-
Subcluster Name: Enter a name for your subcluster.
-
Subcluster type from the dropdown list. Select Primary or Secondary.
-
Number of instances in this subcluster: Select the number of nodes that you want in the subcluster. If you are using the free Community Edition license, you are limited to 3 nodes. If you enter a value greater than 3, you are prompted to enter an upgraded license to continue.
-
Vertica License: Click Browse to locate and upload your Vertica license key file.
If you do not supply a license key file here, the MC uses the Vertica Community Edition license. This license has a three node limit, so the value in Number of instances in this subcluster cannot be larger than 3 if you do not supply a license. See Managing licenses for more information.
-
Node IP setting: Choose a node IP setting. If you choose Public IP, the address is not persistent across instance stop and start.
-
Select Next. On the Specify cloud instance and data storage info screen, Database Depot Path is populated to match the original cluster configuration. Choose or enter a value in the following:
-
EC2 Instance Type: For recommended instance types, see Choosing AWS Eon Mode Instance Types. For a comprehensive list of Vertica supported instance types, see Supported AWS instance types.
-
Database Depot Path: This field is populated with the existing subcluster's depot path.
-
EBS Volume Type: This field is populated with the volume configuration defaults for the associated instance type. Select a new value to change the default.
-
EBS Volume Size (GB) per Volume per Available Node: This field is populated with the volume configuration defaults for the associated instance type. Enter a new value to change the default.
-
Select Next. On the Specify additional storage and tag info screen, the following fields are populated:
-
Database Catalog Path: The path to a persistent storage location.
-
Database Temp Path: The path to an ephemeral storage location if the node instance type includes the ephemeral storage option.
Under each path, there are EBS Volume Type and EBS Volume Size (GB) per Volume per Available Node fields that are populated with volume configuration defaults for the associated instance type. Select or enter a new value to change the default path.
-
Optionally, select Tag EC2 Instances to assign distinctive, searchable metadata tags to the instances in your new subcluster. Existing tags are displayed.
-
Select Next. On Review 'Add Subcluster' information, confirm the configuration details for your new subcluster.
-
Select Add Subcluster to create the subcluster.
After the subcluster is created, The Subcluster page displays. The MC automatically subscribes the nodes in your new subcluster to shards so that the nodes are ready to use.
The following steps add a subcluster on GCP:
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Add Subcluster to open the Add Subcluster window.
-
On Specify Subcluster Information, supply the following information:
-
Subcluster Name: Enter a name for your subcluster.
-
Subcluster type from the dropdown list. Select Primary or Secondary.
-
Number of instances in this subcluster: Select the number of nodes that you want in the subcluster. If you are using the free Community Edition license, you are limited to 3 nodes. If you enter a value greater than 3, you are prompted to enter an upgraded license to continue.
-
Vertica License: Click Browse to locate and upload your Vertica license key file.
If you do not supply a license key file here, the MC uses the Vertica Community Edition license. This license has a three node limit, so the value in Number of instances in this subcluster cannot be larger than 3 if you do not supply a license. See Managing licenses for more information.
-
Node IP setting: Choose a node IP setting. If you choose Public IP, the address is not persistent across instance stop and start.
-
Select Next. Cluster configuration might take a few minutes.
-
On Specify cloud instance and depot storage info, supply the following information:
-
Select Next. On Specify additional storage and label info, supply the following:
-
Database Catalog Path: The path to a persistent storage location.
-
Disk Type: Volume type for the database catalog.
-
Size (GB) per Available Node: Volume size for the database catalog.
-
Database Temp Path: The path to an ephemeral storage location if the node instance type includes the ephemeral storage option.
-
Disk Type: Volume type for the database temp storage location.
-
Size (GB) per Available Node: Volume size for the database temp storage location.
-
Label Instances: Optional. Assign distinctive, searchable metadata tags to the instances in your new subcluster. Existing tags are displayed.
-
Select Next. On Review Information, confirm the configuration details for your new subcluster, and accept the terms and conditions.
-
Select Add Subcluster to create the subcluster.
After the subcluster is created, The Subcluster page displays. The MC automatically subscribes the nodes in your new subcluster to shards so that the nodes are ready to use.
Microsoft Azure
The following steps add a subcluster on Azure:
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Add Subcluster to open the Add Subcluster window.
-
On Specify Subcluster Information, supply the following information:
-
Subcluster Name: Enter a name for your subcluster.
-
Subcluster type from the dropdown list. Select Primary or Secondary.
-
Number of instances in this subcluster: Select the number of nodes that you want in the subcluster. If you are using the free Community Edition license, you are limited to 3 nodes. If you enter a value greater than 3, you are prompted to enter an upgraded license to continue.
-
Vertica License: Click Browse to locate and upload your Vertica license key file.
If you do not supply a license key file here, the MC uses the Vertica Community Edition license. This license has a three node limit, so the value in Number of instances in this subcluster cannot be larger than 3 if you do not supply a license. See Managing licenses for more information.
-
Node IP setting: Choose a node IP setting. If you choose Public IP, the address is not persistent across instance stop and start.
-
Select Next. Cluster configuration might take a few minutes.
-
On Specify cloud instance and depot storage info, supply the following information:
-
Virtual Machine (VM) Size: Select the instance type. For a comprehensive list of Vertica supported instance types, see Recommended Azure VM types and operating systems.
-
Database Depot Path: This value is populated to match the original cluster configuration.
-
Managed Disk Volume Type: Volume type for each node. This value is populated with the volume configuration defaults for the associated instance type.
-
Managed Disk Volume Size (GB) per Volume per Available Node: Volume size for each node. This value is populated with the volume configuration defaults for the associated instance type.
-
Select Next. On Specify additional storage and label info, supply the following:
-
Database Catalog Path: The path to a persistent storage location.
-
Managed Disk Volume Type: Volume type for the database catalog.
-
Managed Disk Volume Size (GB) per Available Node: Volume size for the database catalog.
-
Database Temp Path: The path to an ephemeral storage location if the node instance type includes the ephemeral storage option.
-
(E16_v4 VMs only) Managed Disk Volume Type: Volume type for the database temp storage location.
-
(E16_v4 VMs only) Managed Disk Volume Size (GB) per Available Node: Volume size for the database temp storage location.
-
Label Instances: Optional. Assign distinctive, searchable metadata tags to the instances in your new subcluster. Existing tags are displayed.
-
Select Next. On Review Information, confirm the configuration details for your new subcluster.
-
Select Add Subcluster to create the subcluster.
After the subcluster is created, The Subcluster page displays. The MC automatically subscribes the nodes in your new subcluster to shards so that the nodes are ready to use.
On-premises
For an Eon Mode database on-premises, you can use MC to create additional subclusters. MC displays all available Vertica hosts that are not part of the database. It configures the ones you select to become the nodes in the new subcluster in your database.
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Create Subcluster at top left. MC opens the Create Subcluster wizard.
-
In the first screen, respond in the following fields:
-
**Subcluster Name:**Enter a name for the new subcluster.
-
**Subcluster type dropdown (unlabeled):**Select Primary or Secondary.
-
**Select nodes that will be added to a subcluster:**Select from the list of IP addresses. MC displays all available Vertica hosts within the cluster that are not currently members of a database.
-
**Confirmation:**Click the Confirmation check box to indicate that you want to create the named subcluster, to include the Vertica hosts you selected as nodes.
-
After you click the Confirmation check box, the Proceed button becomes active. Click Proceed.
MC displays a progress screen while it creates the requested subcluster. Wait for all steps to complete.
See also
Subcluster action rules in MC
4 - Rebalancing data using Management Console
Vertica can rebalance your subcluster when you add or remove nodes.
Vertica can rebalance your subcluster when you add or remove nodes. If you notice data skew where one node shows more activity than another (for example, most queries processing data on a single node), you can manually rebalance the sublcluster using MC if the database is imported into the MC interface.
On the Management Console Manage page in the Subclusters tab, click Rebalance above the subcluster to initiate the rebalance operation.
During a rebalance operation, you cannot perform any other activities on the database, such as start, stop, add, or remove nodes.
5 - Subcluster action rules in MC
The table below summarizes when each subcluster action is available for the primary subcluster or a secondary subcluster.
The table below summarizes when each subcluster action is available for the primary subcluster or a secondary subcluster.
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
In the cloud
The explanations in this table apply to subcluster actions in the cloud. For the differences on-premises, see On-Premises further below.
|
Subcluster Action |
Primary Subcluster |
Secondary Subcluster |
|
Add Subcluster |
Allowed.
Must include at least one node. The subcluster cannot be empty.
Vertica recommends having only one primary subcluster.
You can add a second primary subcluster in order to stop the original primary. Be sure to make the replacement primary subcluster at least one node larger than the original. (If you make them the same size, they both count equally toward the quorum, and stopping either would violate the quorum, so you cannot stop either one. For more information, see Data integrity and high availability in an Eon Mode database.)
|
Allowed. Creates a new subcluster.
Provisions cloud instance(s).
Adds nodes to that subcluster.
Defaults to minimum of one node.
|
|
Rebalance
- This button applies to shard subscriptions in Eon Mode.
|
Always allowed.
Note
When you scale down a subcluster, Vertica rebalances the shards automatically, whereas when you scale up a subcluster, you must rebalance the shards yourself.
|
Always allowed.
See note for primary subcluster.
|
|
Start Subcluster
- Includes starting cloud instances if not already running.
|
Available if primary subcluster is stopped. |
Available if:
|
|
Stop Subcluster
- Includes stopping cloud instances.
|
Stop Subcluster is available for the primary subcluster only under certain conditions:
-
Theprimary subcluster must be running.
-
One or more additional primary subclusters must exist in the database.
-
It must be true that stopping this primary subcluster will shut down less than 50% of the primary nodes in the database.
|
Available if running. |
|
Scale Up
- Adds cloud instances which become added nodes.
|
Always allowed.
- Vertica adds nodes that are the same instance type as the existing nodes that are already in the target subcluster.
|
Always allowed. |
|
Scale Down
-
Removes nodes.
-
Terminates instances.
|
Allowed only under the following conditions:
-
If K-safety is >= 1, the remaining number of nodes after scaling down the primary subcluster must be >= 3.
-
The number of nodes you remove must be fewer than half the nodes.
|
Same as for primary. |
|
Terminate Subcluster
|
Available if another primary subcluster exists in the database. |
Always allowed.
- Removes subcluster entry from SUBCLUSTERS table.
|
On-premises
When you start or stop a subcluster in an Eon Mode database on-premises, MC starts or stops the subcluster nodes on the Vertica host machines, but not the machines themselves.
When you scale up a subcluster on-premises, the MC wizard displays a list of the available Vertica host machines that are not currently part of a database. You select the ones you want to add to the subcluster as nodes, then confirm that you want to scale up the subcluster.
When you scale down a subcluster on-premises, MC removes the nodes from the subcluster in the database, but does not terminate the Vertica host machines. The hosts are now available for scaling up other subclusters.
6 - Starting and stopping subclusters in MC
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, the tool bar displays the available subcluster actions above each subcluster.
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, the tool bar displays the available subcluster actions above each subcluster. For example, the screen capture below shows the available actions for the default subcluster, which is also the primary subcluster: Rebalance, Stop (grayed out), Scale Up, Scale Down, and Terminate (grayed out).
Note
Terminate Subcluster is available for Eon Mode databases only in the cloud, not on premises.

Why are some actions grayed out?
Stop and Terminate are grayed out in this example because if you stopped or terminated the only primary subcluster, the database would shut down. For each subcluster, Stop displays if the subcluster is currently running, or Start displays if the subcluster is currently stopped. Both Stop and Terminate are grayed out if their execution would be unsafe for the database.
Starting a subcluster in the cloud
You can start any subcluster that is currently stopped.
-
In the Manage > Subclusters tab, locate the subcluster you want to start.
-
Just above it on the right, click Start.
-
In the Start Subcluster screen, click the check box to confirm you want to start the subcluster.
MC displays a progress screen while the startup tasks are executing.
-
When all the tasks are checked, click Close.
The Manage > Subclusters tab shows that your subcluster is started and its nodes are up.
Stopping a subcluster in the cloud
Important
Stopping a subcluster does not warn you if there are active user sessions connected to the subcluster. This behavior is the same as stopping an individual node. Before stopping a subcluster, verify that no users are connected to it.
You can stop a primary subcluster only if there is another primary subcluster in the database with node count greater at least by 1 node, to maintain K-safety.
You can add a second primary subcluster in order to stop the original primary. Be sure to make the replacement primary subcluster at least one node larger than the original. (If you make them the same size, they both count equally toward the quorum, and stopping either would violate the quorum, so you cannot stop either one. For more information, see Data integrity and high availability in an Eon Mode database.)
You can stop a secondary subcluster anytime, to save money on cloud resources.
-
In the Manage > Subclusters tab, locate the subcluster you want to stop.
If the Stop button is displayed but grayed out, you cannot stop this subcluster because doing so would shut down the database.
-
Just above the subcluster on the right, click Stop.
-
In the Stop Subcluster window, click the check box to confirm you want to stop the subcluster.
MC displays a progress screen while the subcluster stopping tasks are executing.
-
When all the tasks are checked, click Close.
The Manage > Subclusters tab shows that your subcluster is stopped and its nodes are down.
Starting or stopping a subcluster on premises
When you start or stop a subcluster in an Eon Mode database on-premises, MC starts or stops the subcluster nodes on the Vertica host machines, but not the machines themselves.
See also
Subcluster action rules in MC
7 - Scaling subclusters in MC
You can scale an Eon Mode subcluster up or down, to increase or decrease the number of nodes in the subcluster.
You can scale an Eon Mode subcluster up or down, to increase or decrease the number of nodes in the subcluster. This lets you add compute capacity when you need it, and reduce it to save money or redirect resources when you don't.
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
Scaling up in the cloud
When you scale up a subcluster, MC adds one or more cloud instances to your database cluster as hosts, and adds them to your subcluster as nodes.
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Scale Up immediately above the subcluster you want to enlarge. MC launches the Scale Up wizard.
-
Wait a moment or two while MC pre-populates the fields on the Enter AWS Credentials and preferences screen with your credentials, then click Next.
-
On the Specify Subcluster information screen, enter the number of instances you want to add to the subcluster in Number of Instances to Add. MC pre-populates the number of existing hosts in the cluster.
-
Click Browse and select your Vertica license to insert in the license field, then click Next.
-
The Specify cloud instance and data storage info screen has fields that specify the cloud instance and data storage information. MC sets all the fields to the same values as the existing instances in your subcluster. Select Next to accept the existing values.
-
The Specify additional storage and tag info screen displays any tags you specified for your instances when you created the database cluster. You can use the same tags for the instances you are adding, or use the fields on the screen to add new tags for these instances. You can keep and apply or delete the existing tags. If you delete tags, they are not used for the instances you are adding now. When you are done modifying the tags, click Next.
-
MC displays the Review 'Scale Up' information screen for your approval. If the information is correct, click Scale Up to add the instances to the subcluster.
-
Wait until all operations on the progress screen show check marks, then click Close.
Scaling down in the cloud
When you scale down a subcluster, MC removes the requested number of nodes from the subcluster, and removes their hosts from the database cluster. It then terminates the underlying cloud instances. Scaling down a subcluster is allowed only when doing so will not cause the database to shut down.
For details on when Scale Down is or is not available for a subcluster, see Subcluster action rules in MC.
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Scale Down above the subcluster to launch the Scale Down page:
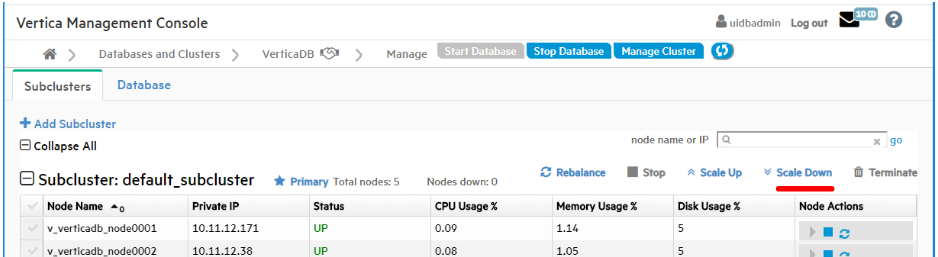
-
In the Number of hosts to remove field, enter the number of hosts you would like to remove from the subcluster.
-
Under Confirmation, click the checkbox to affirm that you want to scale down the named subcluster, and terminate the instances the nodes were using.
-
Click Scaledown Subcluster.
The scale down operation may take a little time. When it finishes, the progress screen displays the details about the removed nodes and their hosts and the terminated instances.
-
When all steps show check marks, click Close.
Scaling on-premises
When you scale up a subcluster on-premises, the MC wizard displays a list of the available Vertica host machines that are not currently part of a database. You select the ones you want to add to the subcluster as nodes, then confirm that you want to scale up the subcluster.
When you scale down a subcluster on-premises, MC removes the nodes from the subcluster in the database, but does not terminate the Vertica host machines. The hosts are now available for scaling up other subclusters.
8 - Terminating subclusters in MC
The Terminate action for subclusters is available for Eon Mode databases only in the cloud.
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
In the cloud
The Terminate action for subclusters is available for Eon Mode databases only in the cloud.
You can terminate any subcluster that will not cause the database to go down. You can terminate:
Terminate a subcluster
-
On the Manage > Subclusters tab, click Terminate immediately above the target subcluster.
-
In the Terminate Subcluster window, click the check box to confirm you want to delete the chosen subcluster and terminate its instances.
-
Click Terminate Subcluster.
MC displays a progress window that shows the steps it is executing to terminate the subcluster.
-
When all the steps are checked, click Close.
On-premises
The Terminate action for subclusters is not available for Eon Mode on-premises. You can stop a subcluster on-premises, provided doing so will not bring down the database. You cannot terminate a subcluster on-premises, because terminating a subcluster stops the nodes and then terminates the cloud instances those nodes reside on. MC cannot terminate on-premises Vertica host machines.
To free up some of the Vertica host machines in an on-premises subcluster, scale down the subcluster.
See also
Subcluster action rules in MC
9 - Node action rules in MC
The table below summarizes when each node action is available for nodes in the primary subcluster or in a secondary subcluster.
The table below summarizes when each node action is available for nodes in the primary subcluster or in a secondary subcluster.
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
For Enterprise Mode databases, MC supports these actions:
Note
In the cloud on GCP, Enterprise Mode databases are not supported.
|
Node Action |
Primary Subcluster |
Secondary Subcluster |
|
Start Node
Starts instance if needed.
|
Always allowed. |
Always allowed. |
|
Stop Node
Stops the instance on a cloud platform.
|
-
Allowed when K-safety is >=1. After the node is stopped, there must be 3 or more remaining UP nodes.
-
Not allowed when K-safety is 0.
|
-
Allowed when K-safety is >=1. After the node is stopped, there must be 3 or more remaining UP nodes.
-
Allowed when K-safety is 0.
|
|
Restart Node |
|
|
|
The Remove Node action has been deleted from existing actions for all nodes. Use Scale Down subcluster instead. |
When you start or stop a node on-premises, MC starts or stops the node in the database, but does not start or stop the Vertica host machine. The Restart Node action is not available for on-premises Eon Mode databases.
See also
Starting, stopping, and restarting nodes in MC
10 - Starting, stopping, and restarting nodes in MC
In MC you can start, stop, and restart nodes in a subcluster in your database.
In MC you can start, stop, and restart nodes in a subcluster in your database. This allows you to tailor the amount of compute power you are using to the current demands for the workload assigned to that subcluster.
For Eon Mode databases, MC supports actions for subcluster and node management for the following public and private cloud providers:
Note
Enterprise Mode does not support subclusters.
For Enterprise Mode databases, MC supports these actions:
Note
In the cloud on GCP, Enterprise Mode databases are not supported.
On the Manage > Subcluster page in the right column, the Node Actions column displays icons that let you start, stop, or restart a node and the underlying cloud machine. Hover over an icon to read the action it performs. If an icon is grayed out, that action is not available for that node.
-
Start Node. Start an individual node in the subcluster.
-
Stop Node. Stop an individual node in the subcluster.
-
Restart Node (GCP only). Restart an individual node in the subcluster.
See also
Node action rules in MC



